Details of the Initiative
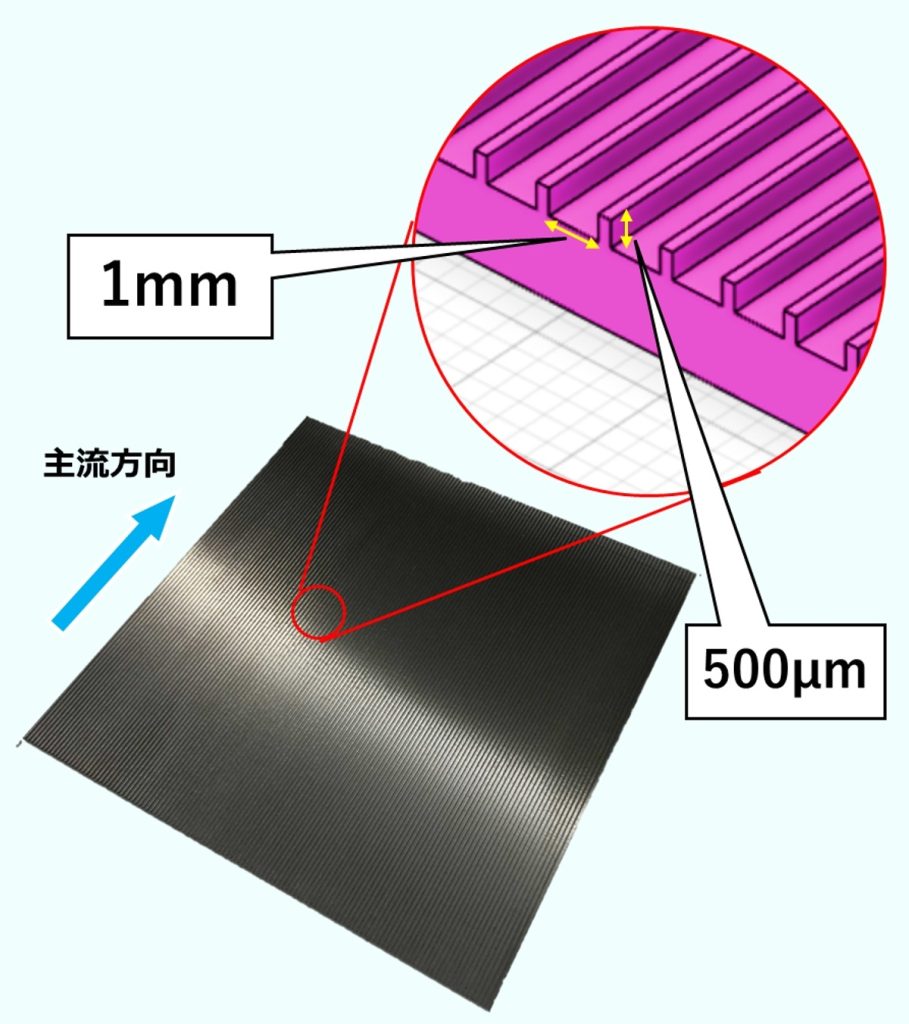
Riblets are structures with fine grooves on their surface that reduce the frictional resistance of fluid flow more effectively than smooth surfaces, contributing to energy conservation and reduced environmental impact. Improving maintenance methods will help facilitate the broader use of riblets in society. When dust accumulates in the concave areas of riblets and cannot be properly cleaned owing to surface irregularities, their resistance-reducing efficiency may deteriorate. To address this issue, our laboratory is researching how water-repellent coatings on riblet surfaces can improve cleaning efficiency.
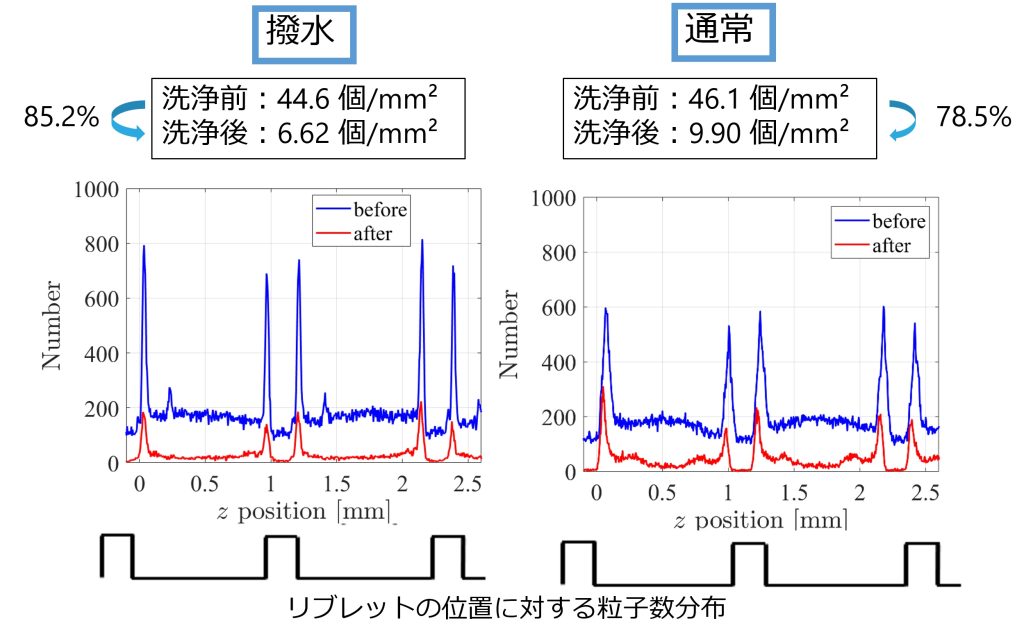
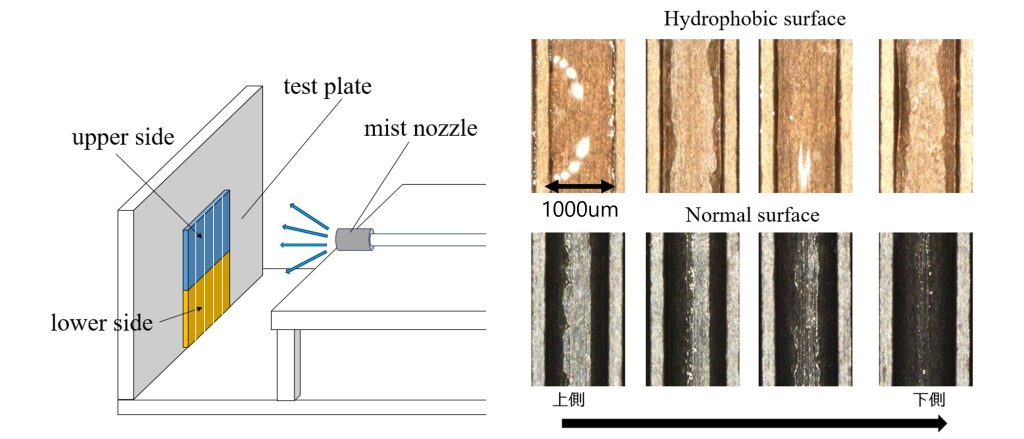
As shown in the photo, we conducted an adhesion test on particulate matter using a riblet plate in the laboratory and verified that the water-repellent coating improved cleaning performance. Furthermore, an examination of water traces, with and without a water-repellent coating, has clarified that differences in water movement within the riblet grooves contribute to improved cleaning efficiency. Since a “flow” is present in many industries and aspects of daily life, optimizing it can help build a sustainable society. That is why our laboratory conducts various studies in this area.